# Network
In this class, we will be using a private Ethereum network, which is a proof-of-work based network. This is how original cryptocurrency networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum are setup and require miners to compute cryptographic puzzles to gain coins.
# Network ID
Ethereum networks have a unique ID (ChainId) to avoid collisions, the one for
ClassNet is: 1337
# Bootnode
enode://d6686e0acb89f5b42d325aaad6a77f6d2c4fe9d2966a45e153ed50051e7617ee22e027ec78e600a2720482399ab74375e97287d357e9f1e4bea473a44c4842ec@iron.gtisc.gatech.edu:30303
To join ClassNet, we provide one bootstrapping node (bootnode (opens new window)). A bootnode is your point of entry onto the network. It is the first node you connect to and it helps you connect to others on the network.
# Exploring Block and Network
BlockScout (opens new window) allows you to view all transactions, accounts and contracts on the network, similar to Etherscan (opens new window) in Ethereum.
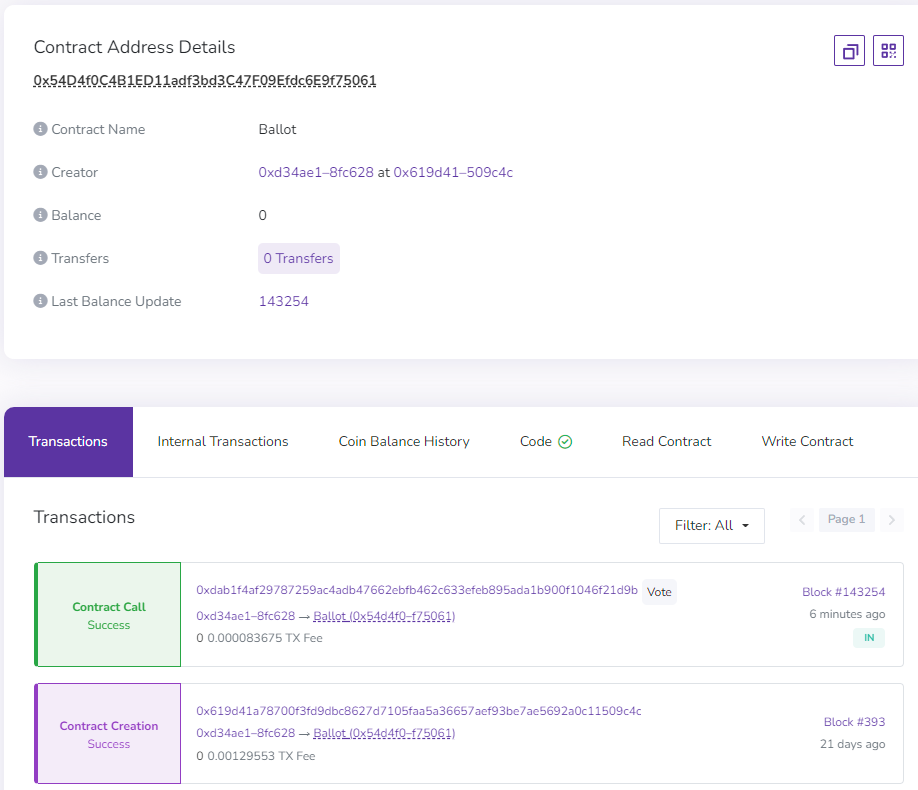
# Contracts
In the following example we can see the address of a contract and the log of
all the transactions it has received. This includes its creation as well as a
call to the Vote method.
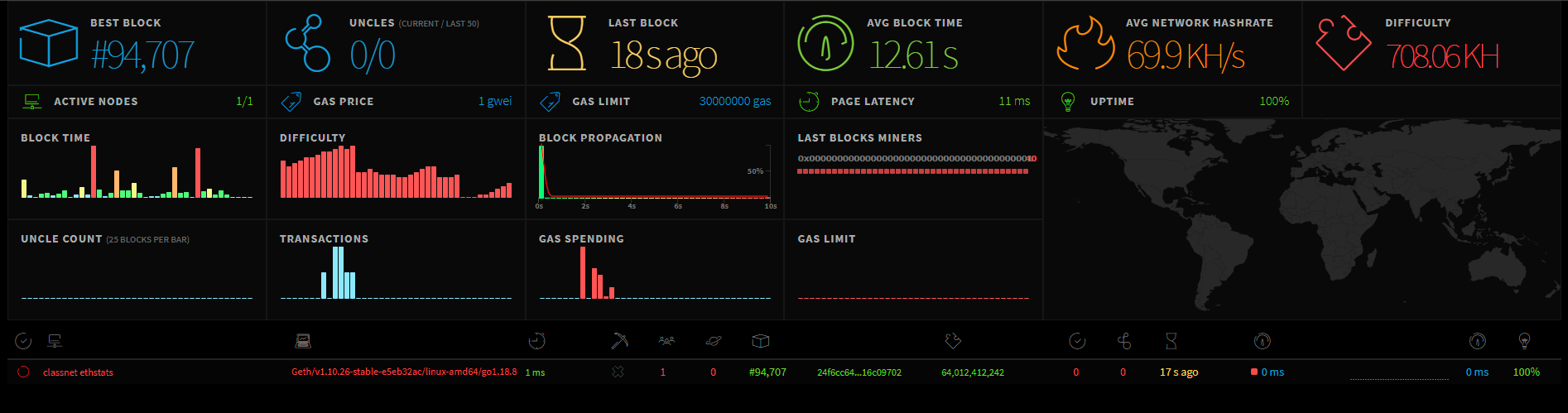
# Miners Statistics
You can also check the state of the network and miners via Eth-netstat (opens new window).
# Faucet Service
If you run out of coins, request some via our faucet service (opens new window). You must login with your Georgia Tech account and can only request once a day.